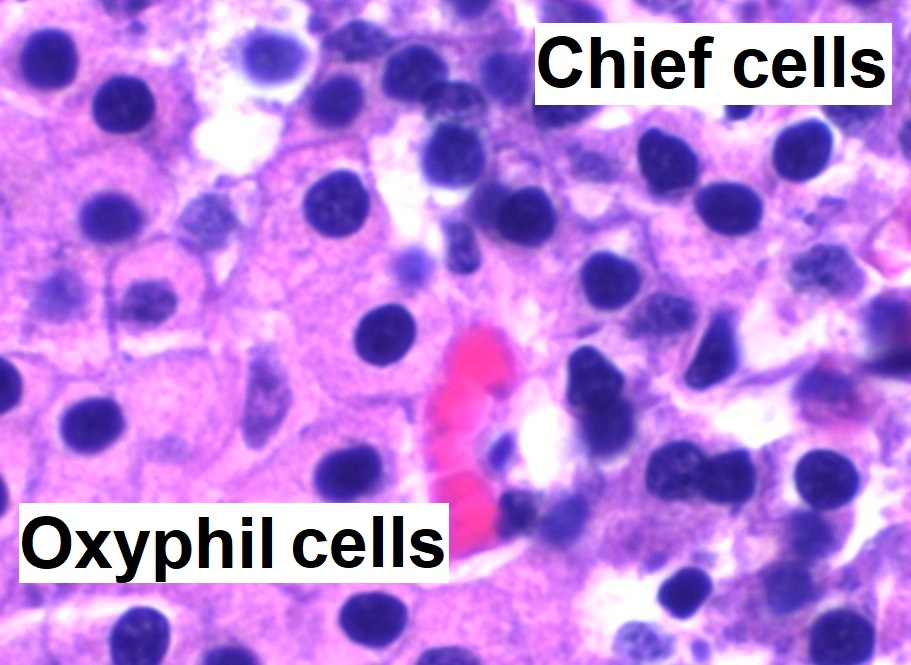
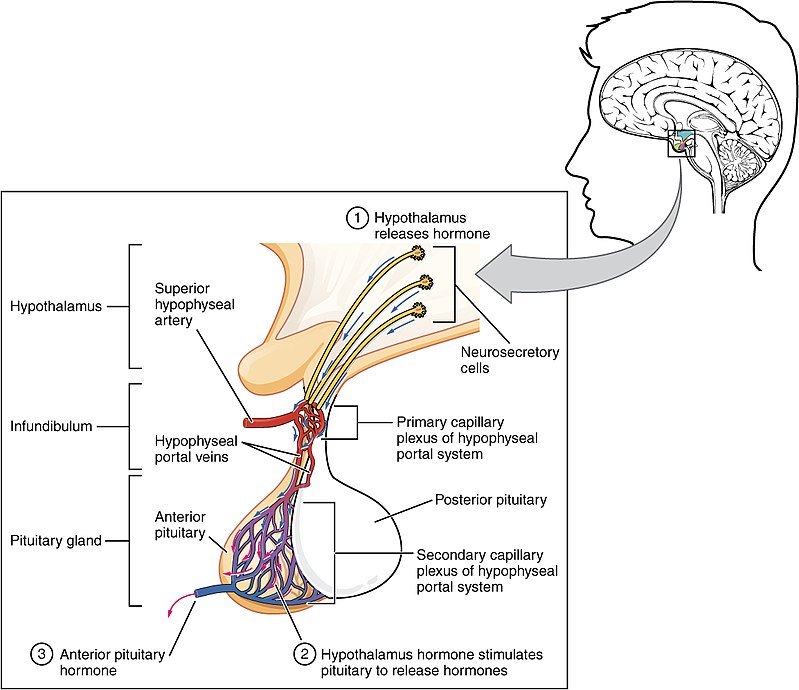
Category: Physiology
Recent Posts
- Titles of Nobility (TON) Prohibitions Around the World

- How TON Breaks Party Chains – Constitutional Fire Version 🔥

- Why We Have a Department of Labor (When TON Says We Shouldn’t Need One)

- What the Titles of Nobility Clauses Could Do to Federal Agencies

- Public vs. Private Hierarchy: Where TON Draws the Line (Airlines & Beyond)

Tags
2025 agriculture alchemy anthropology archaeology art biochemistry biography biology chemistry civil rights crystallography culture duplicate ecology economics endocrinology entertainment entomology folklore genetics geology glossary hematology history immunology law linguistics materials science medicine mythology neurology philosophy physiology politics psychology public health religion reproduction science smoker's paradox symbolism systems theory technology toxicology